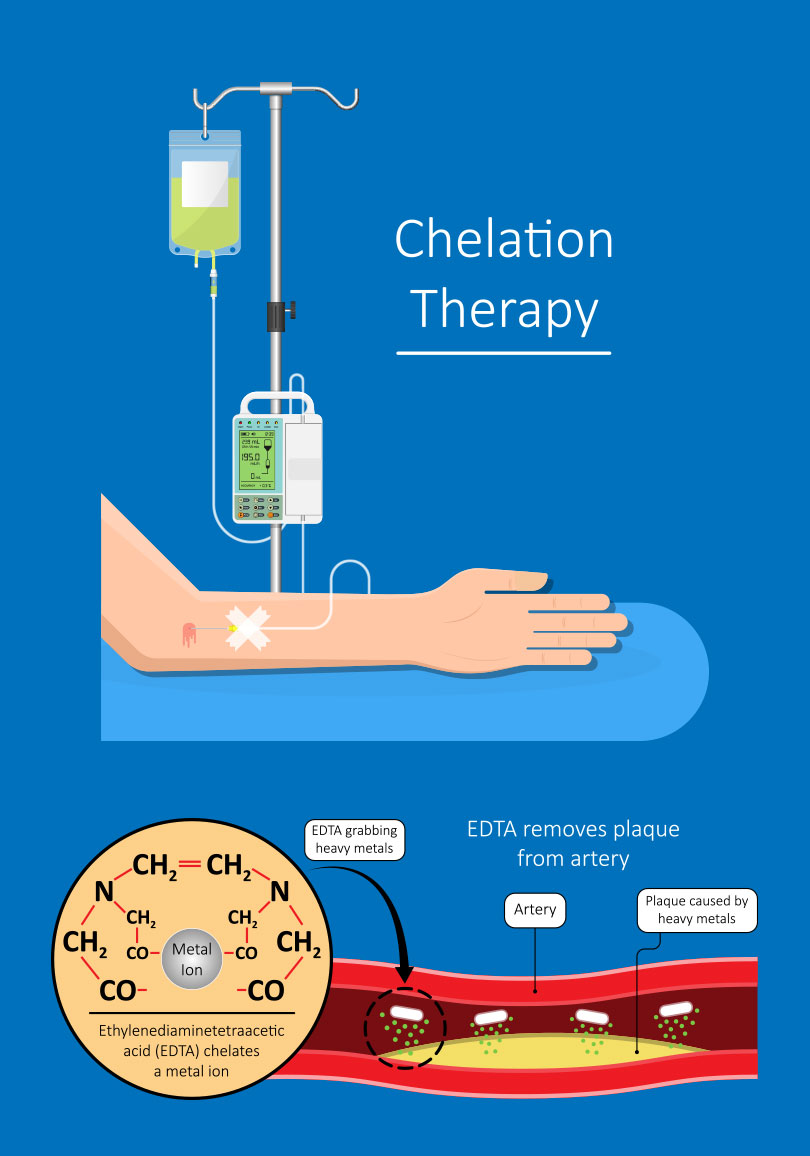
Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy, employing EDTA, is administered intravenously to bind and eliminate heavy metals, reducing potential toxicity. EDTA’s stable complexes facilitate metal excretion through urine, and its antioxidant properties neutralize free radicals. While proven for heavy metal poisoning, ongoing research explores its use in cardiovascular health.
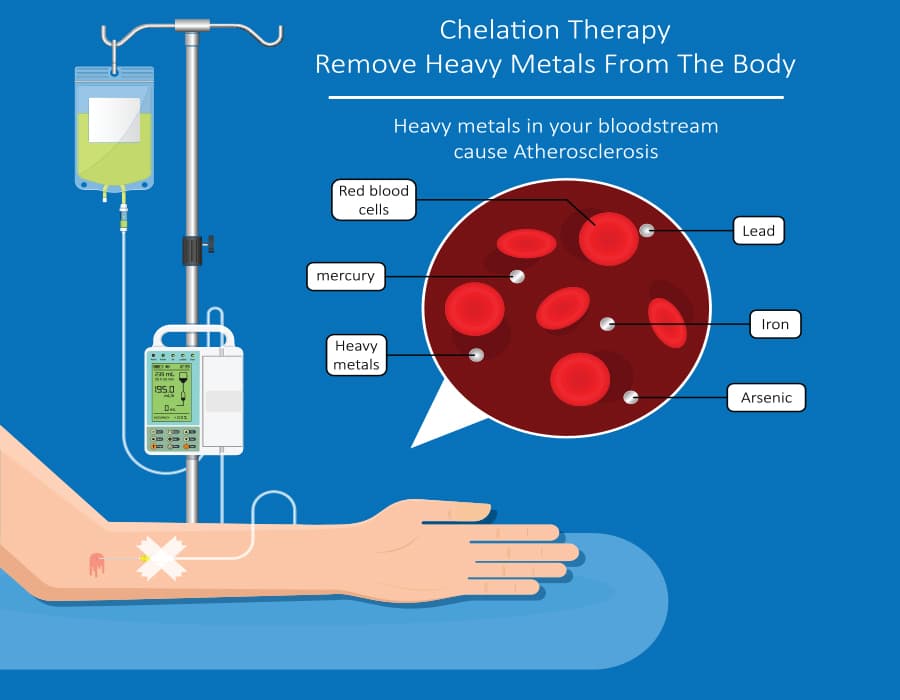

Chelation therapy removes heavy metals:
- Lead: Chelation therapy is particularly effective in treating lead poisoning, a condition often associated with exposure to lead-based paints, contaminated water, or occupational hazards.
- Mercury: Chelation can help eliminate mercury, which may present due to dental amalgams, contaminated fish consumption, or exposure in certain occupational settings.
- Arsenic: Although less common, chelation therapy may used to address arsenic toxicity, often linked to contaminated water, certain foods, or industrial exposure.
- Cadmium: Chelation therapy can aid in the removal of cadmium, typically associated with industrial exposure, smoking, or certain dietary sources.
- Iron: In cases of iron overload disorders such as hemochromatosis, chelation therapy may employed to reduce excess iron levels.
Chelation Treatment For These Three Conditions:
- Autism:
Chelation therapy has been suggested for treating autism, attributing the condition to mercury in childhood vaccines, a notion discredited by studies. Despite such disproven connections, some healthcare providers advocate metal removal for potential improvement in autism symptoms.
- Alzheimer’s Disease:
Alzheimer’s Disease is characterized by the accumulation of abnormal proteins known as tau and beta-amyloid in the brain, causing damage. Presently, there is no known treatment capable of halting or reversing the progression of this disease. There is a hypothesis among some researchers that the buildup of metals such as copper, iron, and zinc could also contribute to Alzheimer’s disease. In such a scenario, chelation therapy might be considered a potential treatment option.
- Heart Disease:
Heart Disease occurs when fatty deposits, known as plaques, develop in the arteries, leading to a narrowing and reduced flexibility of blood vessels. These plaques contain calcium, and the chelating drug disodium EDTA is designed to bind to this mineral. The concept behind chelation therapy is to clear calcium from the blood vessels, aiming to remove plaques as well.
In 2002, the National Institutes of Health conducted a significant study on chelation therapy called TACT. The study revealed that this treatment moderately decreased the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular issues, particularly in individuals with diabetes.